
DAUJAT-CHAVANIEU Martine (CRCE/Inserm) https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5560-1610
GERBAL-CHALOIN Sabine (CRHC/Inserm) https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2549-7899
BRIOLOTTI Philippe (AI/Inserm)
GUIBERT Benjamin (AI / Inserm)
SAIDI Sabrina (IE / Inserm)
ESNAULT Emilie (AI / UM)
AUBERT Clara (AI / UM)
ALAUX Marie (PhD student, resident CHU)
MERHEB Camil (PhD student)
HERRERO Astrid (PU-PH/CHU)
BLANC Pierre (PU-PH/CHU)
NAVARRO Francis (PU-PH/CHU)
Primary human hepatocytes
Detoxication
Metabolism
Nuclear Receptors
Differentiation
Co-culture
Spheroids/organoids
Regeneration
NAFLD/Steatosis
Biotherapy
In vitro models
Isolation and culture of primary human hepatocytes and other cell types from the liver (sinusoidal, Kupffer cells, liver progenitors…)
Micro patterned co-culture, spheroids/organoids, culture under flow
In vitro models of steatosis
Culture and in vitro differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and liver progenitors into hepatocytes
Experimental mouse models
Regeneration, cirrhosis and NAFLD/NASH
Phenotypic and functional characterization
Our work is based on an original model of primary cultures of human adult hepatocytes (PHH) and other hepatic cells (endothelial, sinusoidal, stellate, Kupffer cells, liver progenitors) including mesenchymal cells, which allow investigating several aspects of hepatic physiopathology: metabolism, detoxification, mechanisms of action of carcinogens, hepatitis C virus infection, and stem cell differentiation into hepatocytes. liver detoxication functions, steatosis, cholestasis and liver niche. It combines basic and translational research.
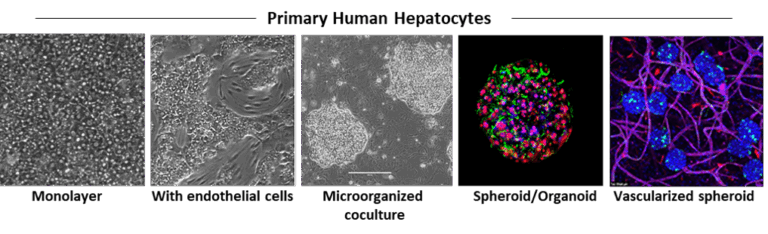
Human hepatocytes are isolated by a two-step collagenase perfusion method, either from organ donor livers that are rejected for transplantation or from liver fragments resected for different medical purposes (metastasis, hepatocellular carcinoma or other pathologies). We have established different experimental conditions for monolayer culture, co-culture with other liver cells, 3D and micropatterned organization and dynamic culture to maintain the phenotype and function of the cells for several weeks.
In Vitro Model of Liver Pathophysiology
The PHH model has been widely used in the laboratory to study xenobiotic and drug metabolism, drug-induced side effects and toxicity, as well as the regulation of drug-metabolizing enzyme genes. This includes investigating the interactions between nuclear receptors such as AhR (Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor), PXR (Pregnane X Receptor), CAR (Constitutive Androstane Receptor), and FXR (Farnesoid X Receptor) with other signaling pathways, and their resulting clinical implications. We are currently investigating the role of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in regulating hepatocyte metabolic functions, bile acid and lipid homeostasis, as well as canalicular organization, and its implications for cholestasis and steatosis. We recently developed a long-term micropatterned co-culture model of PHH with stromal cells to reproduce chronic steatosis, providing a platform to explore NAFLD/NASH mechanisms and test pharmacological and nutritional interventions.
Liver biotherapies
We previously demonstrated that implanting MSC patches on a human amniotic membrane (hAM), placed in direct contact with the remnant liver at the time of hepatectomy, significantly improves animal survival and promotes liver regeneration. As both MSCs and hAM are already used in regenerative medicine, this approach could provide a valuable therapeutic option, particularly for patients undergoing tumor resection with underlying non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or simple steatosis (NAFLD), conditions associated with increased postoperative complications and mortality. This strategy is currently being evaluated for its potential to promote post-hepatectomy liver regeneration in a preclinical murine model of NAFLD/NASH.
In advanced stages of liver failure, orthotopic liver transplantation remains the only effective therapeutic option, yet donor availability is limited. Surgical resection is often not feasible in patients with severely impaired hepatic function. Therefore, therapeutic strategies that stabilize disease progression and delay clinical decompensation are critically needed. In this context, we are developing a tissue construct based on primary human hepatocyte spheroids/organoids, designed to become rapidly vascularized after transplantation into the host omentum or fat pad, and to provide long-term hepatic support in a mouse model of cirrhosis.